 |
Scanning pump probe magnetic light microscope using dual light pulse and concept map of magnetic wave (spin wave)
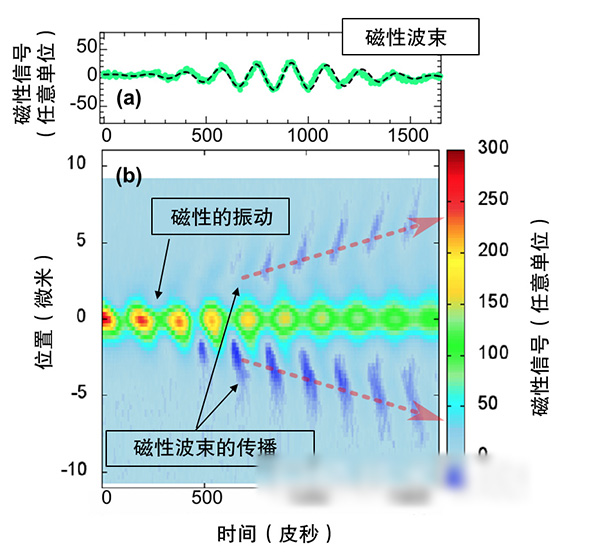
Taking the arrival time and converging position of “pumped†pulsed light as the origin of coordinates, observation of magnetic waves (spin waves) at a position of approximately 3 μm
Tohoku University in Japan announced on July 8, 2016 that it successfully used optical pulses to generate magnetic waves (spin waves) on the surface of metal magnets and successfully achieved high-precision observations. This achievement can contribute to the future development of low-power high-speed information processing equipment using magnetic waves.
Magnetic waves are waves inherent to magnets such as magnets, and they can transmit information without charge flow. Therefore, if high-speed and high-efficiency generation and control of such waves is possible, it is possible to develop high-speed and low-power information processing equipment. . Recent experiments have shown that for magnetic insulators such as garnets and ferrites, femtosecond light pulses can generate magnetic waves. However, in the application of very important metal magnets, no researchers have ever used optical pulses to generate magnetic waves and to observe them clearly and perform quantitative analysis.
The research team of Tohoku University in Japan constructed a scanning pump probe magnetic optical microscope with double-light pulse and high time resolution. The microscope generates magnetic waves from a region approximately 1 micron in radius by concentrating high intensity “pumped†light pulses on the sample. At the same time, another set of weak “pump†light pulses are used to perform time and spatial scanning to detect magnetic changes, and thus the time-resolved measurement of the propagation of the generated magnetic waves can be performed.
This time, the magnetic wave was observed through a 20-nm-thick iron-nickel alloy film. The position of the magnetic beam was clearly observed at a position approximately 3 μm away from the area irradiated by the pump pulse light. It was also found that the magnetic wave propagated about 5 microns in 1500 picoseconds. This situation shows that the magnetic waves generated using the light pulses propagate at a speed of about 3000 meters per second.
The experimental results are consistent with the results predicted by theoretical calculations, and quantitatively demonstrate that the relevant conditions can be explained by physical mechanisms. That is, magnetic waves are ultra-high-speed demagnetization when optical pulses are used to instantaneously heat metal magnetic bodies on a femtosecond time scale. The resulting one.
Using this method, the magnetic properties of various metallic magnetic materials can be studied to help develop materials that generate magnetic waves with higher efficiency and materials that transmit magnetic waves at higher speeds, for the development of these new materials. Contributions, and these new materials will become the basis for using low-power high-speed information processing equipment using magnetic waves. The relevant research results were published on July 1, 2016 (U.S. time) in the "Rapid Communication" column of Physical Review B of the American Physical Society. (Special Contributor: Kudosuke)

Lithium-fluorocarbon button battery products mainly include models of BR2016, BR2025 and BR2032, etc., it has the characteristics of small volume, long storage life, safety, wide working temperature range, and it can work normally under -40~+80℃. Generally, the battery is used in the situations for power requirements with high and low temperature performance, high energy density, such as tire pressure monitor system(TPMS), car keys, industrial control board, computer motherboard, intelligent instrument, unattended operation instrument and other applications.
Button Lithium-fluorocarbon Battery (Li-(CFx)n) models of BR2016
Motherboard button battery,Car keys button battery,High energy density disposable button battery,Button battery models of BR2016,BR2025 and BR2032
Shandong Zhongshan Photoelectric Materials Co., Ltd , https://www.chzsem.com