CNC tools are tools used in machining in machining, also known as cutting tools. The generalized cutting tools include both tools and grinding tools. In addition to the cutting blades, the “CNC tools†also include accessories such as tool holders and holders!
The development of CNC tools plays an important role in the history of human progress. As early as 28 BC to 20 BC, copper knives such as cones, drills, and knives of brass cones and copper had appeared. In the late Warring States period (3rd century BC), copper cutters were made due to the mastery of carburizing technology. The drill bits and saws at the time were somewhat similar to modern flat drills and saws.
However, the rapid development of CNC tools was developed in the late 18th century with the development of machines such as steam engines. In 1783, France's Rene first produced a milling cutter. In 1792, the British Mozley made taps and dies. The earliest literature on the invention of twist drills was recorded in 1822, but it was not produced until 1864.
The tool at that time was made of integral high carbon tool steel with a cutting speed of about 5 m/min. In 1868, the British Mussett made alloy tool steel containing tungsten. In 1898, Taylor and the United States. White invented high speed steel. In 1923, Schletel of Germany invented cemented carbide.
When using alloy tool steel, the cutting speed of the CNC tool is increased to about 8 m/min, and when using high-speed steel, it is more than doubled. When using hard alloy, it is more than twice as high as that of high-speed steel. The surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the workpiece are also greatly improved.
Due to the high price of high speed steel and hard alloy, CNC tools have welded and mechanically clamped structures. Between 1949 and 1950, the United States began to use indexable inserts on turning tools, and soon applied to milling cutters and other CNC tools. In 1938, the German company Degussa obtained a patent on ceramic CNC tools. In 1972, General Electric Company of the United States produced polycrystalline synthetic diamond and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride inserts. These non-metallic tool materials allow the tool to cut at higher speeds.
In 1969, the Swedish Sandvik Steel Plant patented the production of titanium carbide coated carbide inserts by chemical vapor deposition. In 1972, Bangsa and Lagrange in the United States developed physical vapor deposition to coat hard surfaces of titanium carbide or titanium nitride on the surface of cemented carbide or high speed steel tools. The surface coating method combines the high strength and toughness of the base material with the high hardness and wear resistance of the surface layer, so that the composite material has better cutting performance.
CNC tools can be divided into five categories according to the form of the workpiece surface. CNC tools for machining various external surfaces, including turning tools, planing knives, milling cutters, outer surface broaches and boring tools, etc.; hole machining tools, including drill bits, reaming drills, alloy tool boring tools, reamers and internal surface broaches, etc. Thread processing tools, including taps, dies, automatic opening and closing thread cutting heads, thread turning tools and thread milling cutters; gear processing tools, including hobs, gear shaping cutters, shaving cutters, bevel gear machining tools, etc.; cutting tools Including insert circular saw blades, band saws, hacksaws, cutting tools and saw blades, and so on. In addition, there are combined CNC tools.
According to the cutting motion mode and the corresponding blade shape, CNC tools can be divided into three categories. General-purpose CNC tools, such as turning tools, planing knives, milling cutters (excluding formed turning tools, forming planers and forming cutters), boring tools, drill bits, alloy tool reaming drills, reamers and saws; forming CNC tools, this The cutting edge of the tool has the same or nearly the same shape as the workpiece to be machined, such as forming turning tools, forming planers, forming cutters, broaches, cone reamers and various threading tools; Forming the tooth surface of a gear or similar workpiece, such as a hob, a pinion cutter, a shaver, a bevel gear planer, and a bevel gear milling cutter.
The structure of various CNC tools consists of a clamping part and a working part. The clamping part and the working part of the integral structure CNC tool are made on the body; the working part (knife or blade) of the insert structure tool is mounted on the body.
The clamping part of the CNC tool has two types of holes and handles. The perforated NC tool is placed on the spindle or mandrel of the machine tool by means of the inner hole, and the torsional moment is transmitted by means of the axial key or the end face key, such as a cylindrical milling cutter, a sleeve face milling cutter and the like.
CNC tools with handles usually have three kinds of rectangular handles, cylindrical handles and tapered handles. Turning tools, planing knives, etc. are generally rectangular shanks; taper shanks are subjected to axial thrust by taper and transmit torque by friction; cylindrical shanks are generally suitable for smaller CNC tools such as twist drills, end mills, etc. The friction generated produces a torsional moment. Many shank NC tool shanks are made of low-alloy steel, while the working part is made of high-speed steel to butt weld the two parts.
The working part of the CNC tool is the part that generates and processes the chip, including the blade edge, the structure that breaks or rolls the chip, the space for chip removal or chip storage, and the passage of the cutting fluid. Some working parts of the tool are cutting parts, such as turning tools, planing tools, boring tools and milling cutters; some working parts of CNC tools include cutting parts and calibration parts, such as drill bits, reaming drills, reamers, and inner surfaces. Broaches and taps, etc. The function of the cutting part is to cut the chips with a cutting edge. The calibration part is used to polish the machined surface and guide the tool.
The working part of the CNC tool has three types: integral, welded and mechanically clamped. The overall structure is to make a cutting edge on the cutter body; the welded structure is to braze the blade to the steel body; the mechanical clamping structure has two kinds, one is to clamp the blade on the cutter body, and the other is to clamp the blade to the cutter body, and the other The brazed bit is clamped to the body. Carbide tools are generally made of welded structures or mechanically clamped structures; ceramic tools are mechanically clamped.
The geometric parameters of the cutting part of the CNC tool have a great influence on the cutting efficiency and the quality of the machining. Increasing the rake angle reduces the plastic deformation of the rake face when the cutting layer is pressed, and reduces the frictional resistance of the chip flowing through the front, thereby reducing the cutting force and the cutting heat. However, increasing the rake angle will reduce the strength of the cutting edge and reduce the heat dissipation volume of the cutter head.
| Previous page | 1 | 2 | Next page |
A double-convex lens is compose of two convex surfaces, has a positive focal length. Normally Bi-Convex lenses are most suitable where the object and image are on opposite sides of the lens, and are popular for many imaging applications.
Some styles of cylindrical lenses have antireflective coatings to increase the transmission of light through the lens. Fused silica cylinder lenses are ideal for demanding laser machining and medical applications.
We supply kinds of plano-convex Cylindrical Lens,plano-concave cylindrical lens,bi-convex cylindrical lens,bi-concave cylindrical lens,meniscus cylindrical lens,Rod cylindrical lenses,special cylindrical lens etc.Every sizes,materials cylindrical lenses are available according to your detailed parameters.
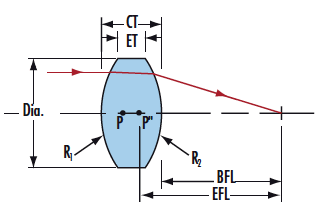
Double Convex Lens
Specification of our cylinderical lens as follow:
*Material: BK7,Ge,UV-grade fuse silica(JGS1,JGS2,JGS3)or other optical materials
*Dimension Tolerance: +0.0 -- -0.1mm
*Center Thickness: +/-0.1mm
*Focal Length Tolerance: +/-1%
*Surface Quality:20/10
*Surface Figure: lambda/2 at 633nm on plano side
*Clear Aperture>90%
*Chamfer: 0.25mm at 45 degree typical
*Coating Optional
Double Convex Lens,Double-Concave Cylinder Lens,Bi Concave Cylindrical Lens,Optical Glass Double-Convex Cylinder Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.realpoooptics.com