At present, most enterprises implement information systems such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) to improve production efficiency. However, many large and complex business systems coexist, the original systems are constantly updated, and the existing systems are constantly expanding. The new business module has brought new problems to the enterprise. How to achieve the 1+l "2" performance through the overall efficient integration of CRM system and ERP system, thus bringing the greatest return on investment for enterprises, has become a hot spot and difficulty for enterprises and IT. Under the traditional economic model, the CRM system and the ERP system are independent of each other, which causes the information flow, value flow and interaction barrier between the enterprises, making the front and back of the enterprise become independent information islands, and the production and decision-making departments can not obtain strong information support. . Therefore, how to establish the system integration of the enterprise before and after the e-commerce environment, so that enterprises, partners and customers are integrated on the same e-commerce platform, strengthen the ties, synergies and analysis capabilities of the company and its partners and customers. One of the keys to competitive advantage.
The integration of business processes in legacy systems has always been a problem that plagues enterprise business and enterprise IT. The current emerging SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture Framework) foundation platform bridges this gap, enabling enterprises to quickly and flexibly change their business processes and maintain the enterprise. Competitiveness. It is in this context that this paper proposes an integration scheme between CRM system and ERP system based on the principle of SOA.
1 Service-oriented architecture framework
1.1 SOA Architecture
SOA is a coarse-grained, loosely coupled service structure that makes enterprises more resilient and flexible. It responds quickly to changes in business requirements and has a well-defined standard interface. The coarse-grained service means that the service performs a larger business function and exchanges more data than fine-grained; the coupling between services means that the service has a neutral interface (no mandatory binding to a specific implementation); A standardized interface means that Web services enable application functionality to be delivered through a standardized interface (WSDL) and can be invoked using standardized protocols (SOAP) based on standardized transport methods (HTTP and JMS).
The core technologies of SOA include: SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), WSDL (Web Service Description Language), and UDDI (Unified Description Discovery and Integration), all represented in standard XML (Extensible Markup Language) documents.
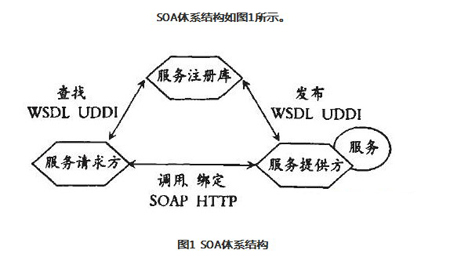
WSDL abstractly describes a service as a collection of endpoints that contain operations performed on a document-oriented or process-oriented message. A number of related concrete endpoints are combined to form a service.
A service provider is a network-addressable entity that accepts and executes requests from service consumers. It publishes the services and interface contracts in the Service to the service registry so that service consumers can access the service.
A service consumer can be an application, a software module, or another service that requires a service. It initiates a query for the service in the service registry, binds the service through the transport, and performs the service function. The service consumer executes the service according to the interface contract.
The service registry is a proponent of service discovery. It contains a repository of available services and allows interested service consumers to find the interface of the service provider.
The operations of Web services mainly include publishing, searching, binding, and calling.
1.2 Enterprise Service Bus
ESB (Enterprise Service Bus) is an enterprise architecture bus. All enterprise services are linked to the bus and published. The enterprise service bus is responsible for managing the service directory, parsing the request method and message format of the service requester, and providing the service. Addressing and forwarding service requests. If there is no enterprise service bus, then the requester of the service must know the address of the service it needs, and must know the corresponding service calling method and message format. Such a call is point-to-point, which is not conducive to the unified management of the service. Conducive to the integration of different format services.
The ESB is a core functional component that must be implemented to build an SOA architecture. ESB generally uses SOAP and HTTP protocols and supports transport protocols such as JMS (Java Message Service), MQ (Message Queue), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), and SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
2 SOA-based integration solution
For enterprises, CRM system and ERP system do not give full play to their use value, which is reflected in two aspects: First, the lack of synchronization and integration of the same and related data in CRM system and ERP system, resulting in a large number of internal enterprises The existence of information silos increases the difficulty of data maintenance. Second, it does not realize the unified integration of the CRM system and the ERP system's respective business processes, and does not realize the end-to-end automatic flow of business processes.
To this end, based on the SOA idea, the integration scheme of CRM system and ERP system is proposed. The SOA integration platform implemented by this solution is the core foundation platform for solving deep problems such as “information islandâ€, “process isolation†and “global invisibility of business processesâ€. In the business layer, process reorganization of the two systems of CRM and ERP; at the service layer, coarse-grained service extraction is carried out with the idea of ​​SOA, and fine-grained demand analysis is performed downward. Through the analysis of the process and use cases, based on the principle of loose coupling between services, select the appropriate granularity to identify and segment the services, extract the service model, and provide the interface. Service is the core of SOA. There are two types of services in this solution: one is to package the functions provided by the original CRM system or ERP system; the other is the newly created service, these two services Components are organized in a certain order to meet the needs of business processes.
The two systems of CRM and ERP are mainly divided into two modes in the process of integration: business integration and data integration. Business integration requires the business processes of the two systems to be reorganized, reanalyzed to form new business processes, and data synchronization in the process. Data integration involves fewer business processes, and only needs to synchronize the corresponding data in the two systems during the information maintenance process. After analysis, sales and procurement operations require business integration; customer information, supplier information, products, and their classification information require data integration.
Expanded metal is sometimes considered an alternative to sheet metal or wire mesh. It combines some of the best features of both-providing a material that is stronger than thin wire mesh and has better air flow and drainage than sheet metal.
Expanded Metal Mesh,Element Expanded Metal Mesh,Aluminum Expanded Metal Mesh,Ss Standard Expanded Metal Mesh
HEBEI KAYI BUILDING MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.kayigrating.com