Antibiotics have been added to feeds to promote the growth and development of livestock and poultry for nearly 60 years, but in order to avoid the proliferation of drug-resistant strains due to the abuse of antibiotics or to increase the residual amount of drugs in animal products, Direct damage to livestock and poultry growth and human health has begun to use more antibiotic feed additives such as tylosin and bacitracin, which are commonly used in dozens of species. At present, although there are many controversies about whether antibiotics should be used in feed, it has been proved that the rational use of antibiotic additives can promote the growth of livestock and poultry and increase the feed conversion rate. At the same time, there are reports that countries that do not allow the addition of antibiotics or other antibacterial growth promoters to feeds will result in increased livestock production costs and reduced profits, as well as problems such as the ecological environment and trade wars between countries. In fact, antibiotic additives are still in a large number of applications. Only by comprehensively understanding and rationally applying them and improving their application level can they fully exert their beneficial effects and avoid harm to human health. This paper intends to give a brief introduction to the role of antibiotic feed additives, growth promoting mechanism and commonly used antibiotic additives for livestock and poultry.
1 role of antibiotic feed additives
The growth-promoting effect of antibiotics on animals was discovered by Stocktadt et al. in the late 1940s. Later, antibiotics such as tetracyclines, macrolides, and β-endosamines were added to feeds to promote growth and increase. Heavy, increase production, and improve the role of feed compensation. In 1950, the US FDA officially approved the addition of antibiotics to feed. The role of antibiotics in the growth and production performance of livestock and poultry is positive and stable, and antibiotic additives have long been used in the livestock and poultry industries in many countries. The growth-promoting effects of various antibiotics have the following common features: (1) the effect on young animals is much more significant than in adult animals; (2) in the case of poor sanitation and incomplete nutrition, the effect is more significant. (3) In terms of use effect, antibiotics are effective for single-stomach livestock such as pigs and chickens, and have poor effects on adult ruminants, and should not be used, but have certain effects on yak (within 6 months of age) and lambs; (4) After using the same antibiotic continuously in the same environment for a period of time, its growth-promoting effect is significantly reduced.
2 antibiotic growth promoting mechanism
The mechanism of growth-promoting action of antibiotics is still not fully understood, and there is some controversy. However, it is generally believed that its growth-promoting effect is not a direct effect and may play an indirect role from the following two aspects. [page_break]
2.1 Health effects
On the one hand, antibiotics inhibit or kill certain pathogens or parasites, thereby preventing and treating bacterial or parasitic diseases. When animals take less than the therapeutic dose of antibiotics, they help the development of immunity in juvenile animals, especially The immune system of the body is still not perfect. The effect on young animals with weak disease resistance is more pronounced. At the same time, it can also save a lot of manpower and material resources due to individual preventive treatment. On the other hand, antibiotics can inhibit the proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the digestive tract and reduce the destruction and consumption of essential nutrients such as vitamins and amino acids by harmful microorganisms.
Under certain conditions, antibiotics can reduce the concentration of ammonia in animal tissues and the environment. In addition, it has been suggested that antibiotics can also reduce the effects of some factors that are unfavorable to animal growth, such as certain chemical components or toxins produced during storage, and improve feed efficiency.
2.2 Nutritional effects
Antibiotics also protect the intestinal wall from microbes or parasites, allowing it to fully absorb nutrients, including histological effects on the gastrointestinal tract and preventing or reducing microbial production of toxins and harmful metabolites in the gut. Studies have found that some microorganisms or parasites can thicken or damage the intestinal wall of animals, and the use of antibiotics inhibits these pathogens, thereby maintaining or restoring the function of the intestinal wall. In addition, some antibiotics can increase the growth of beneficial bacteria in the body. For example, streptomycin can increase the growth of certain yeasts in the chicks, thereby promoting the synthesis of essential nutrients in the birds. These changes are beneficial to the absorption and utilization of nutrients. Some people think that after application of antibiotics, the intestinal villi of animals will become longer, which is conducive to the absorption of nutrients. At the same time, antibiotics have a saving effect on nutrients, especially B vitamins, or that antibiotics have an effect of increasing appetite and increasing feed intake. It also stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete hormones, promote development and so on.
3 commonly used antibiotic additives for livestock and poultry
For a long time, people use antibiotics shared by humans and animals. These antibiotics have a large amount of absorption, and there are many residues in the body. Long-term use is easy to cause pathogens to produce drug resistance, which has adverse consequences for the prevention and treatment of human diseases. Therefore, various antibiotic additives for livestock and poultry with good effects and low toxicity have been developed at home and abroad, including peptides, phosphorylated polysaccharides, macrolides, polyethers, and aminoglycosides. These antibiotic additives for livestock and poultry have common characteristics:
(1) The anti-pathogen (microorganism or parasite) has strong activity, does not interfere with the micro-ecological balance of the normal intestinal flora, promotes the weight gain of livestock and poultry, and improves the feed conversion rate;
(2) chemically stable, mainly in the intestinal tract, the original shape or metabolites are not absorbed by the tissue, no residue or very little residue in the animal products;
(3) Bacterial or parasitic bacteria are not easy to develop resistance, and do not cross-resistance with other antibiotics;
(4) low toxicity, large safety range, harmless to humans and animals, no side effects such as teratogenic, carcinogenic, mutagenic;
(5) There is no adverse effect on the palatability of the feed. [page_break]
3.1 peptides
It is a special antibiotic additive for livestock and poultry that is currently developing rapidly and is used more. Including bacitracin, colistin, enramycin, virginiamycin, thiopeptin, avomycin.
(1) Bacitracin ( )
In 1943, American Johnson was found in Bacillus subtilis. It is currently produced from the culture of Bacillus licheniformis. It is commonly used in clinical zinc salts. It can inhibit the formation of microbial cell walls and protein synthesis, and the antibacterial spectrum is similar to penicillin. In the United States in 1960, the use of bacitracin zinc as a feed additive was first approved. It was approved in 1990 and is one of the most widely used antibiotic feed additives. It is used in livestock and poultry feeds with little dosage and no stopping requirements. Its 1 mg is equivalent to 42,000 U.
Recommended feeding dose: pig 4~40mg/kg, chicken 4~20mg/kg, cattle (within 3 months) 10~100mg/kg, and cattle (3~6 months old) 4~10mg/kg.
(2) Colistin ( )
In 1980, Japan’s Oyama Co. was obtained from the culture solution of Bacillus polymyxa. It has three components, A, B and C. It is often used as a sulfate with good stability. It is also called sulfate antibiotics, polymyxin sulfate. E. It has a strong inhibitory effect on G-bacteria, and C has a weak effect on G+ bacteria. Japan and the United States first approved as feed additives, and China has no production at present (it is reported that Tianjin Xinxing Veterinary Medicine Factory has been put into production, will be put on the market - editor's note), but it was approved for import in 1986. Colistin has a good synergistic effect with bacitracin zinc, and its use in a fixed ratio (1:5) can make up for its shortcomings of kidney poisoning, such as universal fertilizer.
Recommended feeding dose: 5~40mg/kg for lactating calves, 2~20mg/kg for broilers (within 10 weeks) (additive titer for two antibiotics), and 2~40mg/kg for pigs (within 2 months) price). Laying hens are banned and the drug withdrawal period is 7 days.
(3) Enramycin (am)
In 1967, the Takeda Pharmaceutical Research Institute of Japan was obtained from the actinomycete culture solution. It mainly consists of two components, A and B. It is also commonly used as the hydrochloride salt, also known as amphotericin and enmycin. It has strong activity against G+ bacteria. Japan approved the use in 1974, China approved the Japanese import in 1988, and there is currently no production in China.
Recommended feeding dose: chicken 1~10mg/kg (potency), piglet 2.5~20mg/kg. Laying hens are banned and have no drug withdrawal period.
(4) Virginiamycin ( )
The American Shike Pharmaceutical Factory is obtained from the Streptomyces vinifera culture solution, which mainly consists of the M1 body of the macrolide and the S1 body of the cyclic polypeptide. The antibacterial range of M1 and S1 is different, and the virginiamycin is the two. The complex, also known as virginiamycin. It only inhibits G+ bacteria, and can also improve the absorption of yellow pigment in feed by broilers, and increase egg production rate and yellowness of egg yolk. The United States, Japan and the European Community have approved the use as feed additives for livestock and poultry. China has no production, but it has been approved for use. Its premix is ​​called Stafaco.
Recommended feeding dose: pig 10~20mg/kg, chicken 2~5mg/kg, 45kg or more pigs are forbidden. Can not be used in combination with other antibiotics, the drug withdrawal period of 1 day.
(5) Thiopeptin (amipeptin)
In 1969, Fuji-sawa Corporation of Japan was obtained from the culture solution of the genus tateyamensis of the genus Nocardia, and was a mixture of type A (Al~A2) and type B. It has strong antibacterial effect on G+ bacteria and mycoplasma. It is harmful to the liver of animals and should not be used in large quantities for a long time. China has not yet approved the use.
Recommended feeding dose: broiler chicken and chickens growing at 10 weeks old 0.6~10mg/kg, pigs 1~20mg/kg. Laying hens are banned and the drug withdrawal period is 7 days.
(6) Avoparcin [Avoparcin]
It is obtained from the culture solution of S. candius, and has strong antibacterial effect on G+ bacteria and some G-bacteria. It has not been approved for use in China (the EU has banned the use of avomycin in pan-Europe since April 1997). Feed Additives - Editor's Note). [page_break]
3.2 Phosphorylated polysaccharides
It is a kind of antibiotics containing phospholipids, mainly for C+ bacteria. At present, the antibiotics of such antibiotics have been approved as feed additives in Europe, America, South America and Asia, and the antibiotics in this category also include Northmycin, big grammycin (also known as code carbopol, has been eliminated).
(1) Flavomycin,
In 1965, the United States Hoechst company was obtained from the Streptomyces griseus culture medium, and at least four components: A, B1, Japan, Ba, C, mainly A. Also known as yellow phospholipids, zebramycin. It has a growth-promoting effect on cattle, pigs, chickens and rabbits, and relieves stress. Combined with polyethers, it can also improve the quality of chicken. China approved the import in 1993, and its premixed product name is Fullerwang.
Recommended feeding dose: broiler chicken, laying hens 1~5mg/kg, lactating pigs 5~20mg/kg, other pigs 2~10mg/kg, fur animals 1~4mg/kg, calves 6~16mg/kg. No medicine period.
(2) Quebecmycin (Quedenycin)
In 1965, the acidic substance obtained from Streptomyces culture in Canada has high stability of sodium salt, also known as ketomycin. It is a special feed additive for chickens and piglets.
Recommended mixed dose: 1~20mg/kg[page_break]
3.3 Polyether class
For a class of veterinarians dedicated to anti-coccidial antibiotics, also has a broad-spectrum antibacterial, growth-promoting effect, also known as ionophore antibiotics, commonly used as feed additives including monensin, salinomycin and rasagines.
(1) Monensin (Monensin)
In 1967, Eli Lilly and Company was obtained from the culture medium of streptomycin streptozotocin. Its sodium salt was called Rumensin. It is widely used in the beef cattle fattening period in more than 40 countries, such as the United States. It is mainly used to inhibit acetic acid. Fermentation, reducing methane production, increasing the proportion of propionic acid in rumen fermentation, is highly toxic to equine animals, and is not effective for dairy cows. China approved imports in 1998 and can also be produced domestically. The company's 10% premixed product from Eli Lilly and Company is called Desire ~100. This product can not be combined with dimetridazole, tylosin, tamarind, and oleandomycin.
Recommended feeding dose: yak 17~33mg/kg, lamb 10~30mg/kg, chick 77~120mg/kg, young turkey 60~100mg/kg. No medicine period. Laying hens are banned.
(2) Salinomycin (aminomycin)
Japan Scientific Research Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. was obtained from the culture of white streptococci in 1968. The trade name is excellent in spermatozoa (10%). Many countries have approved it as a growth promoter for growing pigs. China imported it in 1985. Do not use with tylosin or oleandomycin, otherwise it will cause poisoning.
Recommended feeding dose: pig 300mg/kg, beef cattle 200mg/ton. The drug holiday period is 0~1 days.
(3) Lasalicid (amalocid)
Roche was acquired in 1951 by a strain of Streptomyces lansin, also known as rasakaloxifene. In 1979, the United States approved its sodium salt as an anticoccidial agent. In recent years, the United States has listed it as a beef cattle growth promoter under the trade name Boratec. It is said to be superior to rumin in promoting growth and is safe for horses. China is temporarily unable to produce, but has approved the import of Avalec, a premix of Swiss soil.
Recommended feeding dose: yak, horse 30 ~ 40mg / kg, lamb 20 ~ 60mg / kg, laying hens disabled, drug withdrawal period of 3 days.
3.4 macrolides
Tylosin, a special additive for livestock and poultry in this class of antibiotics, was obtained from Lilly's Streptomyces cinnarum culture in 1955 by the American Lilly Company. The trade name is Tylan, which is often used as feed additive. It is tylosin phosphate and is used as a drinking water to add tylosin tartrate. It is effective against G+ bacteria and some G-bacteria, mycoplasma and spirochetes, and has better safety than bacitracin, but it is more resistant to drug resistance. It can be synergistic with other additives (such as hygromycin B).
Recommended mixed dose: pig (within 4 months old) 10~40mg/kg, pig (4~6 months old) 5~20mg/kg, chicken (within 8 weeks old) 4~50mg/kg. The drug holiday is 5 days.
3.5 aminoglycosides
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are used as feed additives for livestock and poultry for the A and hygromycin B.
(1) Destomycin A (Japan) Meiji Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. was obtained from actinomycete broth in 1965. The trade name is Destonate, which is an antibiotic worm, a variety of pigs and chickens. The nematode has a good repellent effect and also has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect. Japan, the United States, and the European Community have approved as additives. They are produced in small quantities in China. They can be used for pigs, broilers, and pre-laying hens under 4 months of age. They can be used together with various antibiotics to promote each other.
(2) Hygromycin B (HygeonycinB)
American Lilly Company was obtained from Streptomyces hygroscopicus culture in 1958, also known as Hyaluronic Acid B. The trade name is Hygromix. It can inhibit G-bacteria, some G+ bacteria and actinomycetes, and can effectively kill pigs. Some nematodes in chickens can be combined with other antibiotics. It is a safer animal-specific antibiotic and drive. Insecticide. Japan, the United States, Australia and other countries have approved the use of additives.
Recommended feeding dose: broiler chicken, laying hens, 9.9~13.2mg/kg for pigs under 50kg for 8 weeks. Broiler broiler 3 days, pig 2 days.
Colour Laminated Glass is very similar to Clear Laminated Glass but with the addition of a coloured interlayer. These allow for a rich palette of colour permutation, ranging from subtle transparent and translucent colours to opaque. Our colour laminates are manufactured using float glass as standard although also available in specialist glasses including low iron (crystal clear) and a variety of body tints (blue, bronze and grey). The type and thickness of the glass will have an effect on the colour chosen.
Laminated glass is produced when two or more glass lites are permanently bonded with one or more plastic interlayers (PVB) using heat and pressure. The glass and interlayers can be a variety of colors and thicknesses. Laminated glass is often called [safety glass" because it meets the requirements of various code organizations. Laminated glass can be broken, but the fragments tend to adhere to the plastic layer and remain largely intact, reducing the risk of injury. Laminated glass can be incorporated with heat-strengthened and Tempered Glass to further increase impact resistance.
It can be made into clear laminated glass, colored laminated glass, Triple Laminated Glass, laminated Insulated Glass , printed laminated glass, Low-E Laminated Glass, toughened laminated glass, tempered laminated glass and so on. Colored laminated glass can be reach by colored PVB, color tinted glass, and also printed laminated glass, depend on customer's design request.
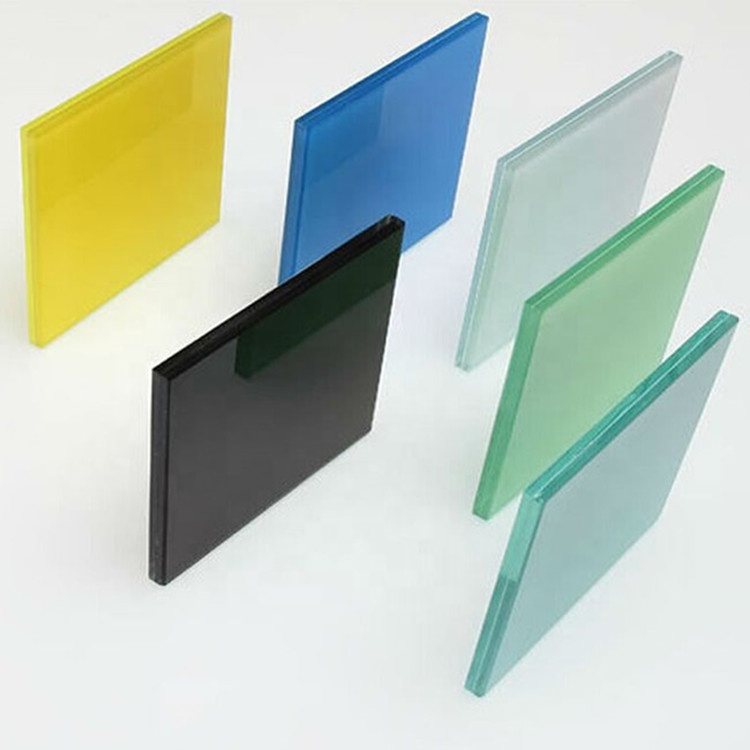
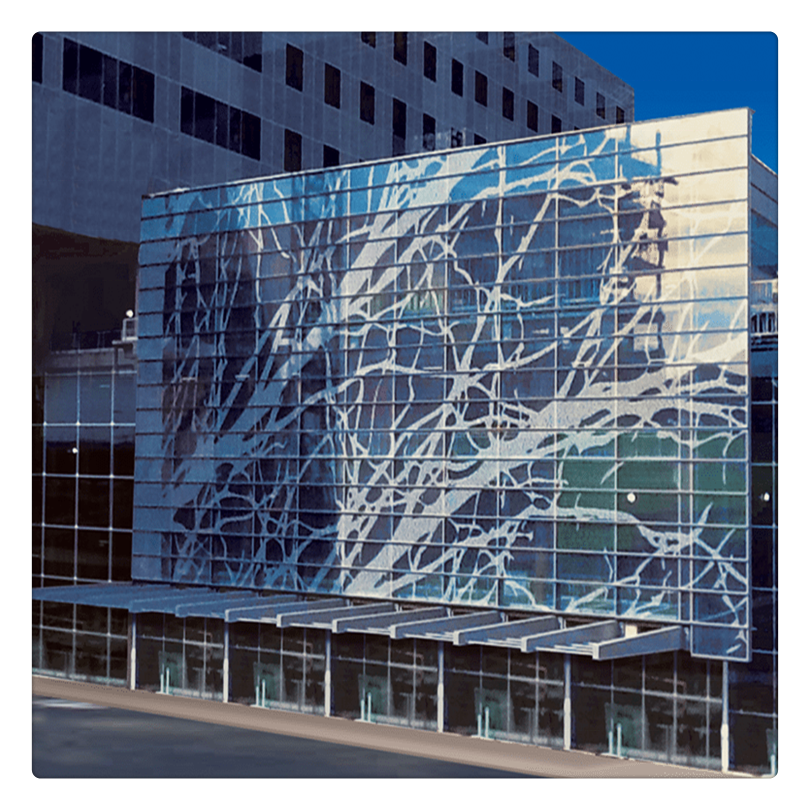
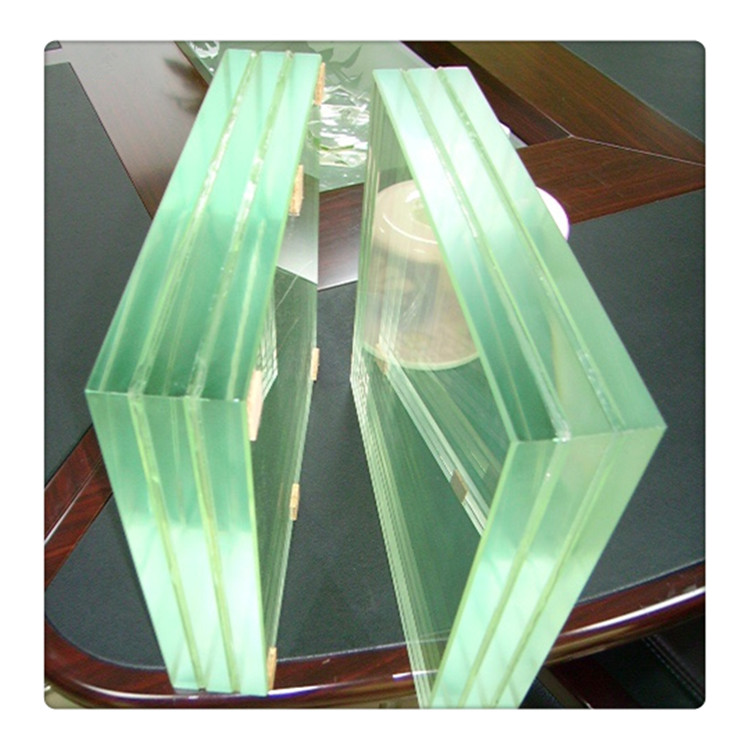


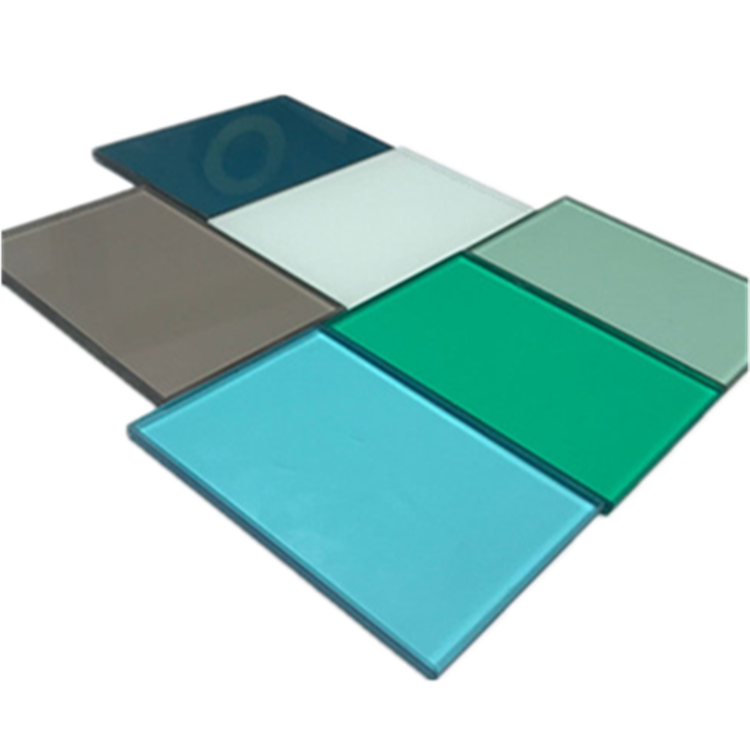


Laminated building glass,laminated glass price,laminated glass cut to size,toughened laminated glass,white laminated glass
Shanghai Lead Glass Co.,Ltd , https://www.leadglazing.com